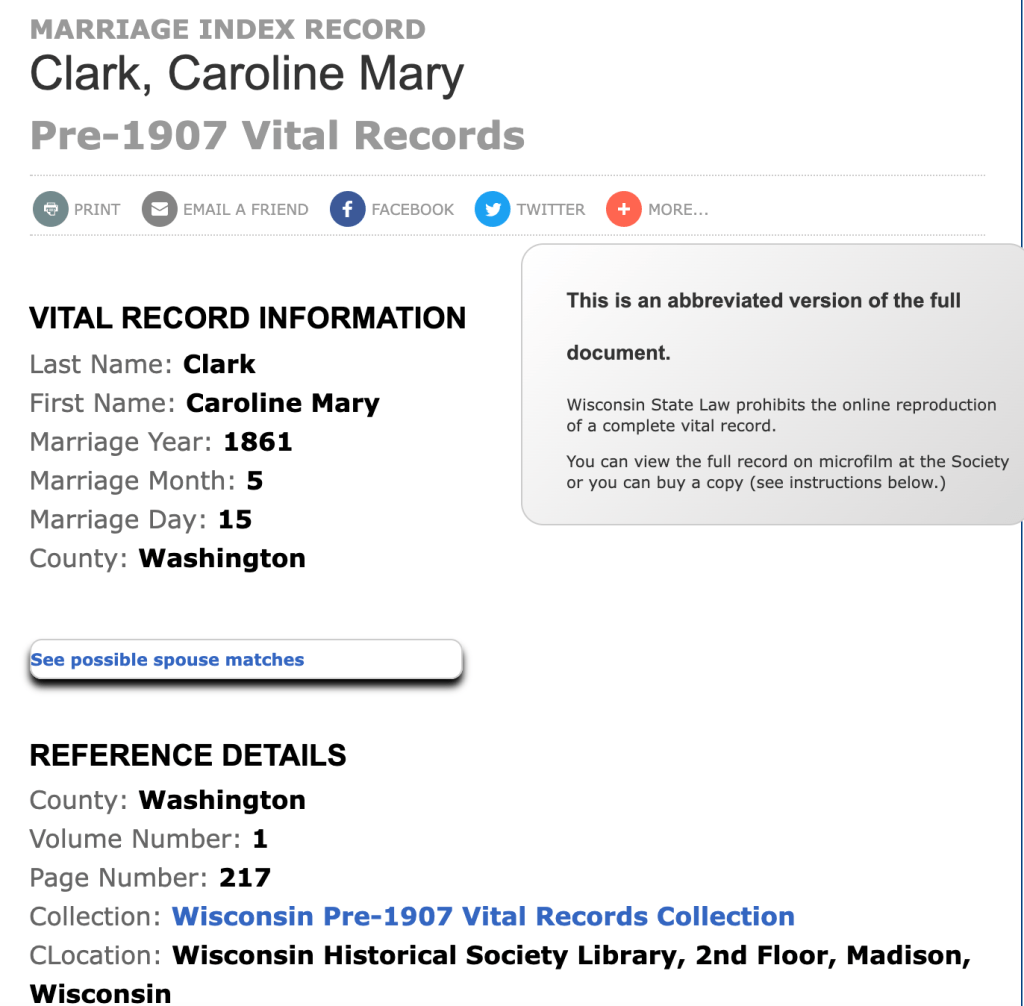
Updated February 22, 2022 to fix a few minor typos, and to add a link to a brief history of American samplers, with an illustrated list of 73 of the 137 American samplers in the Textile Collection of the National Museum of American History.
In addition to raising and educating her children, a 19th-century farm wife like Mary Turck Clark had many other responsibilities, including planning and tending a farm garden, preserving its produce, preparing daily meals for the family and hired hands, and keeping the farm house clean and organized. And Mary, like many women of her era, probably made some or all of her own and her family’s clothes.
The sewing arts
Like most girls of her era, Mary Turck (born in New York, 1821) probably learned the craft of needlework from her mother and, perhaps, as part of her school education. When a young girl like Mary mastered some of the many practical and decorative sewing stitches, she might demonstrate her proficiency by making a sampler.
A sampler might feature simple examples of sewn letters, numbers and perhaps a popular saying or Bible verse. But many samplers were more complex and artistic. An accomplished embroiderer might produce an elaborate sampler featuring detailed images and texts, as in this 1829 sampler from Connecticut.

Thompson, Mariette (1817-1851), [Sampler with family register], 1829. Yale Art Gallery, public domain. Click to open larger image in new window.
Continue reading