Lest We Forget
Our annual Memorial Day post, first published in 2020. Updated for 2023 with new information about Evander B. Bonniwell’s service.
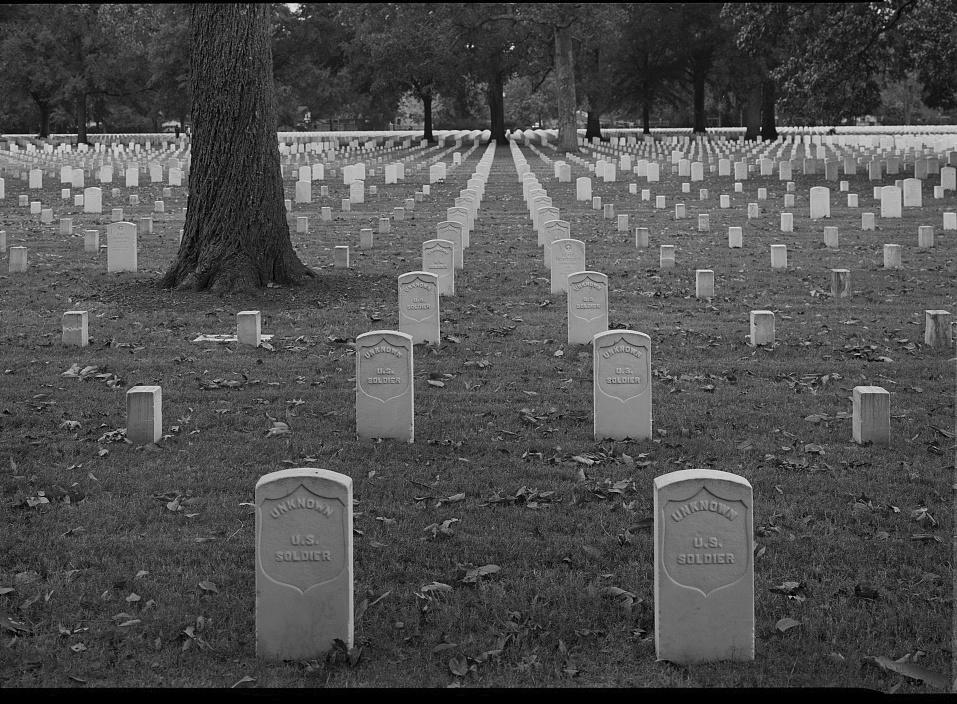

Graves of Unknown Union Soldiers, Memphis National Cemetery, photo by Clayton B. Fraser, (Library of Congress), public domain. Memphis National Cemetery is the final resting place of Mequon’s Watson Peter Woodworth, and almost 14,000 of his Union Army comrades.
Today is the day our nation officially observes Memorial Day. For many Americans, Memorial Day represents “the first day of summer,” and is traditionally celebrated with trips to the lake, picnics, parades, and sales on cars, appliances, and other consumer goods.
But for many of us, Memorial Day remains rooted in its origins as Decoration Day. The first national observance was in 1868, when retired general John A. Logan, commander and chief of the Grand Army of the Republic—the Union veterans’ organization—issued his General Order Number 11, designating May 30 as a memorial day “for the purpose of strewing with flowers or otherwise decorating the graves of comrades who died in defense of their country during the late rebellion, and whose bodies now lie in almost every city, village, and hamlet churchyard in the land.”
On this Memorial Day, let’s take a moment to remember what this day truly represents.
Continue reading