OK, this “Monday: Map Day!” is a few days late (and has been updated since posting, see notes 7 & 8). But I needed a bit more time to edit this beautiful and historic map of the County of Kent for you. Kent was home to Mequon’s pioneering Bonniwell family and their kin for almost 150 years, and taking a close look at its geography may prove helpful for understanding the family and its history, including some of the earlier inscriptions in the Bonniwell family Bible.
Cantivm Vernacule Kent, 1665
Let’s begin with a view of the complete, original map. It was made in 1665, just before James Bonniwell (1636-1709) moved his family from Sutton-Courtney, Berkshire, in south-central England, to Kent, in the southeast.1 As always, I encourage you to click the images to view higher-resolution versions of each map in a new window. Take some time to zoom in and out and scroll around. There’s a lot to see, so I’m going to keep the commentary to a minimum.2
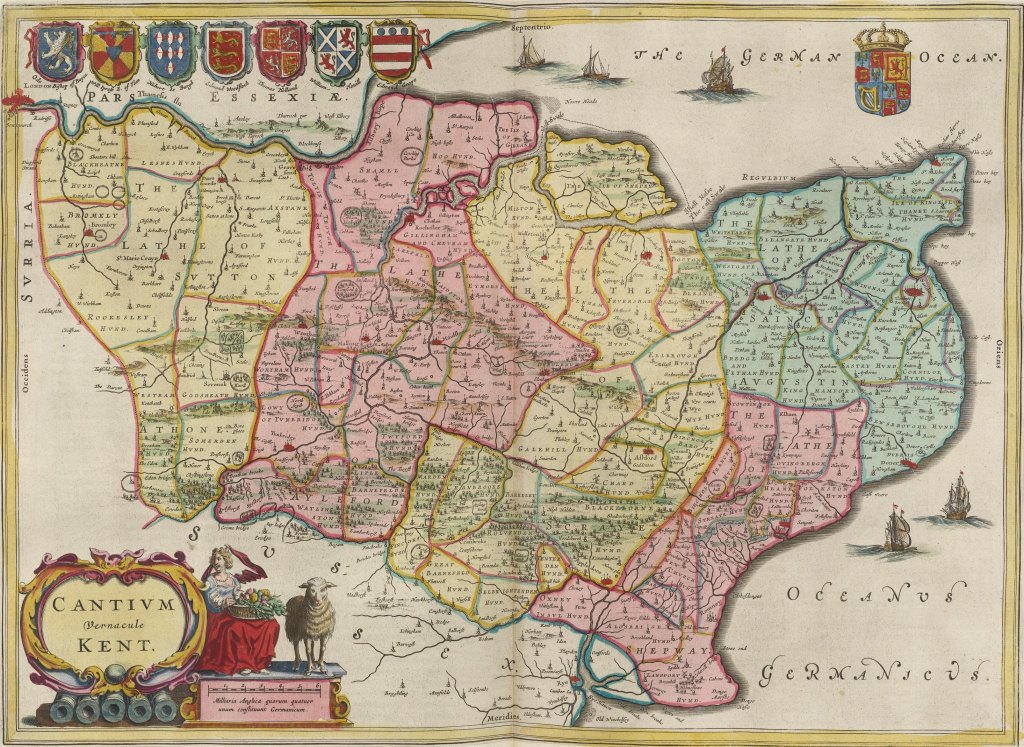
This 1665 map, titled Cantivm Vernacule Kent [Cantium, in the vernacular, Kent], is part of a much larger work, Joan Blaeu’s magnificent Atlas Maior Sive Cosmographia Blaviana, published in Amsterdam between 1662-1672. This is another amazing map made available online by the David Rumsey Map Collection, whose staff provided this commentary:
Continue reading




